Green Hydrogen UPSC | Types | Uses | Making Of Green Hydrogen : Why In The News ?
- Recently, government has announced the Green Hydrogen mission where the target is to make the country self-reliance in energy by 2047.
What Is Hydrogen ?
- Hydrogen is the lightest and first element on the periodic table.
- Since the weight of hydrogen is less than air, it rises in the atmosphere and is therefore rarely found in its pure form, H2.
- At standard temperature and pressure, hydrogen is a nontoxic, nonmetallic, odorless, tasteless, colorless, and highly combustible diatomic gas.
- Hydrogen fuel is a zero-emission fuel burned with oxygen.
- It can be used in fuel cells or internal combustion engines.
- It is also used as a fuel for spacecraft propulsion.
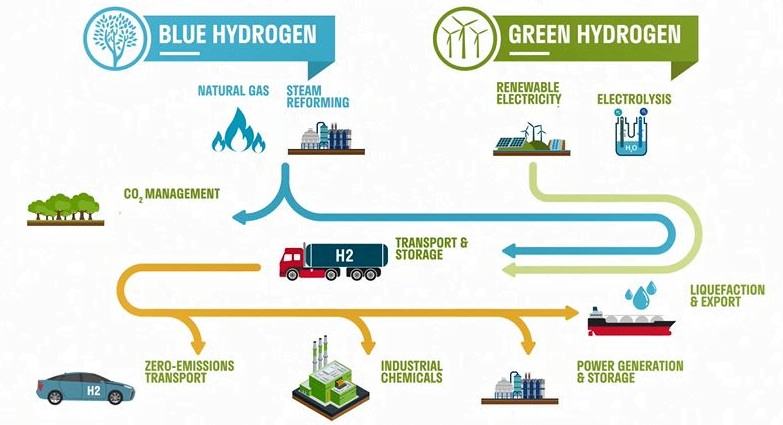
Types of Hydrogen: Green Hydrogen
| Brown Hydrogen |
|
| Grey Hydrogen |
|
| Blue Hydorgen |
|
| Green Hydrogen |
|
Occurrence of Hydrogen:
- It is the most abundant element in the universe.
- The sun and other stars are composed largely of hydrogen.
- Astronomers estimate that 90% of the atoms in the universe are hydrogen atoms.
- Hydrogen is a component of more compounds than any other element.
- Water is the most abundant compound of hydrogen found on earth.
- Molecular hydrogen is not available on Earth in convenient natural reservoirs.
- Most hydrogen on Earth is bonded to oxygen in water and to carbon in live or dead and/or fossilized biomass.
- It can be created by splitting water into hydrogen and oxygen.
Read also : International Solar Alliance | UPSC | Power, Functions
Storage Of Hydrogen :
- Hydrogen can be stored physically as either a gas or a liquid.
- Storage of hydrogen as a gas typically requires high-pressure tanks.
- Storage of hydrogen as a liquid requires cryogenic temperatures because the boiling point of hydrogen at one atmosphere pressure is −252.8°C.
- Hydrogen can also be stored on the surfaces of solids (by adsorption) or within solids (by absorption).
Usage of Hydrogen :
- Hydrogen is used in the synthesis of ammonia and the manufacture of nitrogenous fertilizers.
- Hydrogenation of unsaturated vegetable oils for manufacturing vanaspati fat.
- It is used in the manufacture of many organic compounds, for example, methanol.
- Hydrogen chloride is a very useful chemical and is prepared from hydrogen.
- Hydrogen can reduce many metal oxides to metals by metallurgical processes.
- Hydrogen is used as rocket fuel in many space research activities.
- Hydrogen fuel is being experimented within the automotive industry with hydrogen fuel cells.
What Are The Challenges In Making Hydrogen ?
- The challenge right now is that big electrolyzers are in short supply, and plentiful supplies of renewable electricity still come at a significant
- Storing and transporting the highly flammable gas is not easy; it takes up a lot of space and has a habit of making steel pipes and welds brittle and prone to failure.
- The bulk transport of hydrogen will require dedicated pipelines, which would be costly to build, pressurizing the gas, or cooling it to a liquid.
- High Cost: In a report published last year (using data from 2018), the International Energy Agency put the cost of green hydrogen at $3 to $7.50 per kilo, compared to $0.90 to $3.20 for production using steam methane reformation.
- Loss of Efficiency in every process: Electrolyzer efficiencies range from around 60 percent to 80 percent, according to Shell. The efficiency challenge is exacerbated by the fact that many applications may require green hydrogen to power a fuel cell, leading to further losses.
Current Production Of green Hydrogen :
- Green hydrogen currently accounts for less than 1 percent of total annual hydrogen production.
- The pipeline of green hydrogen electrolyzer projects nearly tripled in the five months leading up to April 2020, to 8.2 gigawatts.
Green Hydrogen Infrastructure in India:
- India was focusing on producing blue and green hydrogen along with blended hydrogen in Compressed Natural Gas (CNG) for various purposes, including transport.
- Through technological advancements, India is blending hydrogen with compressed natural gas for use as transportation fuel as well as an industrial input to refineries.
- 50 buses in Delhi are plying on blended hydrogen in Compressed Natural Gas on a pilot basis.
- The Indian Oil Corporation Limited announced it would set up the country’s first green hydrogen Plant .
- Reliance Energy said that it would invest Rs 600 billion in building factories to produce green hydrogen among other carbon friendly technologies.